Development of AI quantification of body composition database system
 |
 |
|
Wing P. Chan, Professor and Chief Department of Radiology, Taipei Medical University Expertise: MRI, musculoskeletal imaging, spine imaging, oncologic imaging, AI |
Chwan-Lu Tseng, Associate Professor Electrical Engineering, National Taipei University of Technology |
Contents
Abdominal visceral fat and subcutaneous fat can be used to evaluate and predict cancer progression or mortality. When subcutaneous fat decreases and visceral fat increases, patients with colorectal cancer will have a poor survival rate. In the past, the analysis of abdominal fat and muscle regions were used as the quantitative results in one single slice image (the third lumbar spine body L3) to explore the relationship between body fat area and related diseases. It is obvious that there is no sufficient theoretical basis to use the area value of a single slice image to explore its relationship with the diseases; while there is no software that can automatically quantify the 3D abdominal fat volume. At present, most of the tools need to manually circle the periphery of each abdominal fat, which consumes lots of time and energy for the clinical physicians to finish the tasks. The physicians need to manually draw the target lesion on the workstation, and then output the selected region of interest (ROI, Region of Interest) in a specific format. This research is to resolve this clinical pain point.
Anticipated result
We will develop a prototype of integrated AI imaging database system with 3D body fat extraction, trying to develop an automatic quantification of body fat, and establish a clinical cut point of visceral and subcutaneous fat volumes for healthy population of Taiwan.
Benefits to industry
At present, there is no related AI software on the market, and it has the potential to promote the market in Taiwan. Adopting this cut point of normal body fat for healthy population in Taiwan, it will be able to effectively monitor the changes and variations of body fat volume between cancer patients and healthy patients in the future, so as to change the treatment strategies and improve the survival rate of cancer patients.
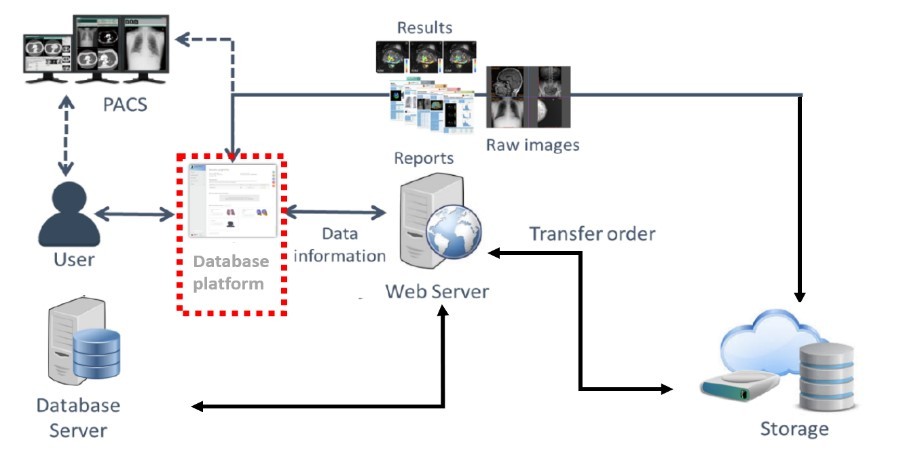
Fig-1. Develop a medical imaging database with the features of image storage, image retrieval and image security. The imaging database platform architecture is shown in the figure above.
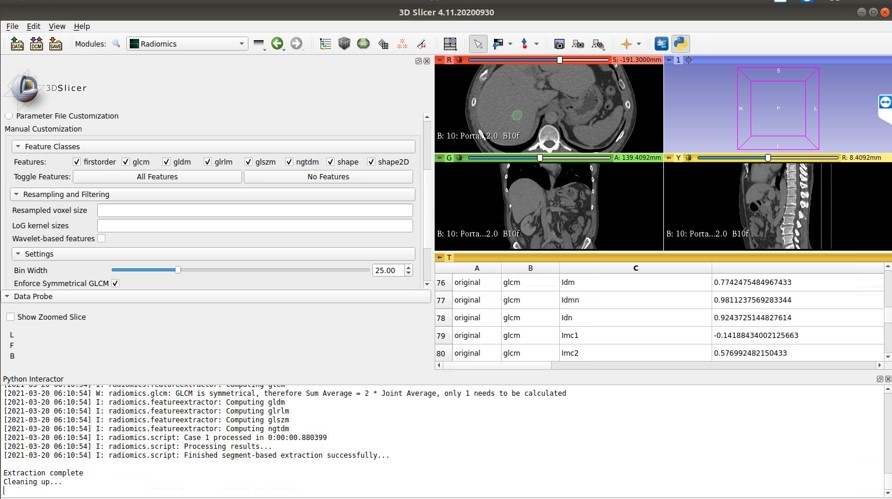
Fig-2. Establish and train the prototype of the new AI based body fat CT platform.
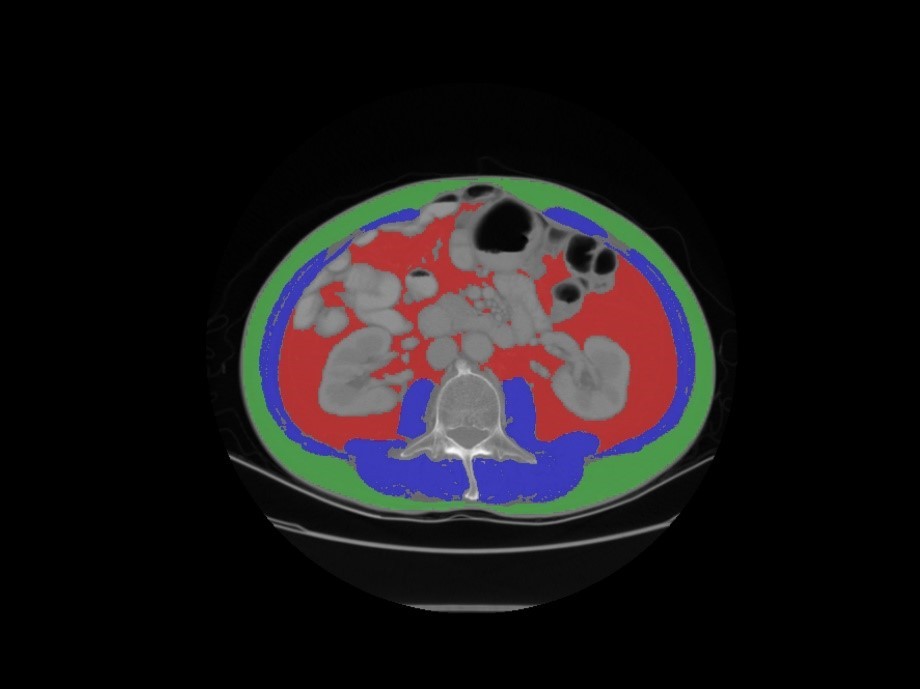
Fig-3. Schematic diagram of the post-processing for 3D body fat volumes in the training procedure.