Rehabilitation monitoring system and method
Rehabilitation monitoring system and method
Prototyping
Professor Name:Yo-Ping Huang
Cooperation Partner:Taipei Veterans General Hospital
Patent:82119-TW-PA
About 8 million people worldwide suffer from Parkinson's disease (PD). PD patients often have gait instability problems. Clinicians and researchers often need a gait analysis system such as GaitRite to assist the measurement. In order to solve the problems faced by the clinicians for the above problems we develop a quantitative system that effectively tracks and monitors the rehabilitation process. Using a set of nine-axis sensors and wearable devices, with a self-developed APP system, to combine with Kinect, microcontroller, nine-axis sensor, multiplexer, Bluetooth equipment, etc., the proposed system can effectively record, track, and monitor rehabilitation progress. The system consists of 10 sensors worn on specific areas to observe the specification of feature angles. There are three main parts of the system. The first is the collection of gait information by the sensor. The second is to integrate the sensing device information and provide interactive functions through the Unity 3D platform. It can record and track the patient's posture information such as flexion, extension, external rotation, and rotation. Finally, the gait information such as the step length and the number of steps is calculated for collecting gait information. The Kinect system can analyze the gait movements instantly, and use the developed algorithm to calculate the stride, the number of steps, the movement distance of the lower limb joints and the range of motion in the joint angle, and the dynamic time warping algorithm. By comparing the relative relationship of gait characteristics in the same distance when the subjects were tested before and after rehabilitation, the system can assist the physical therapists to quantify the effectiveness of the subjects before and after rehabilitation, analyze and quantify the information on the continuous movement of the lower limbs to solve the problem that was limited to the maximum joint position or static rehabilitation assessment. All the action information enables the physician to grasp the real-time status. The functionality of the proposed system is comparable to the professional GaitRite system.

Fig. 1. System Architecture.
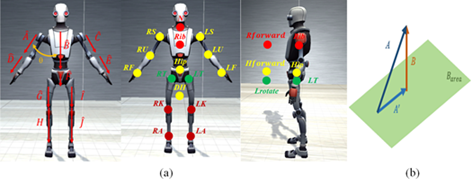
Fig. 2. (a) Definition of the human joint angle. (b) Method of projecting a three-dimensional vector.
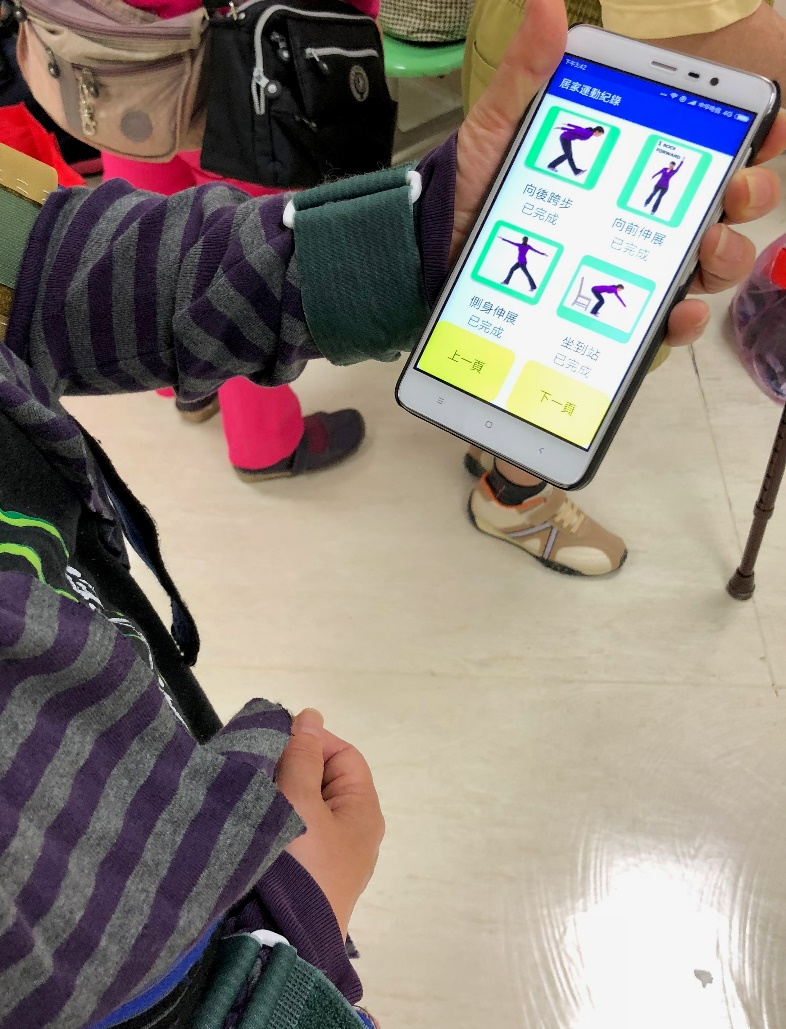

Fig. 3. Patient rehabilitation APP system.
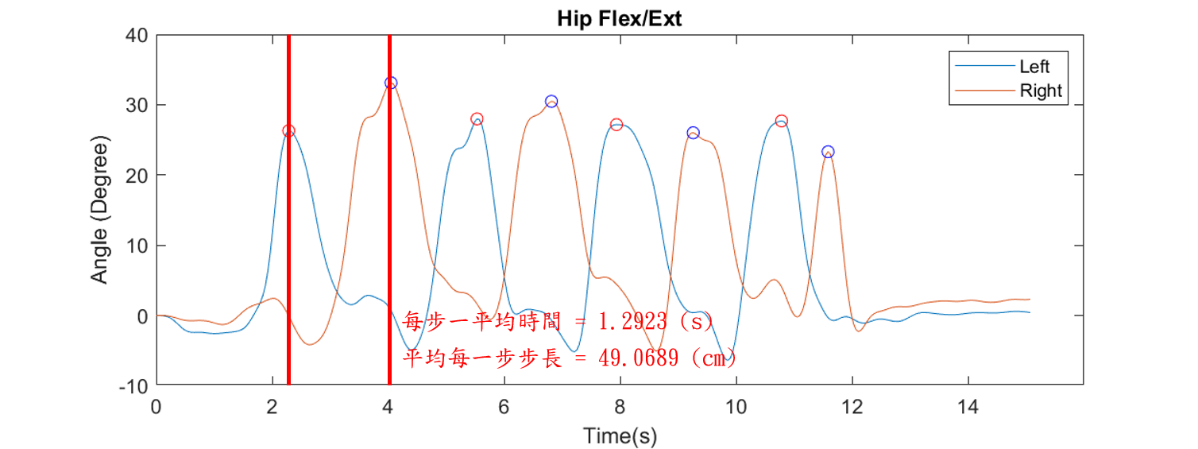
Fig. 4. Gait analysis.
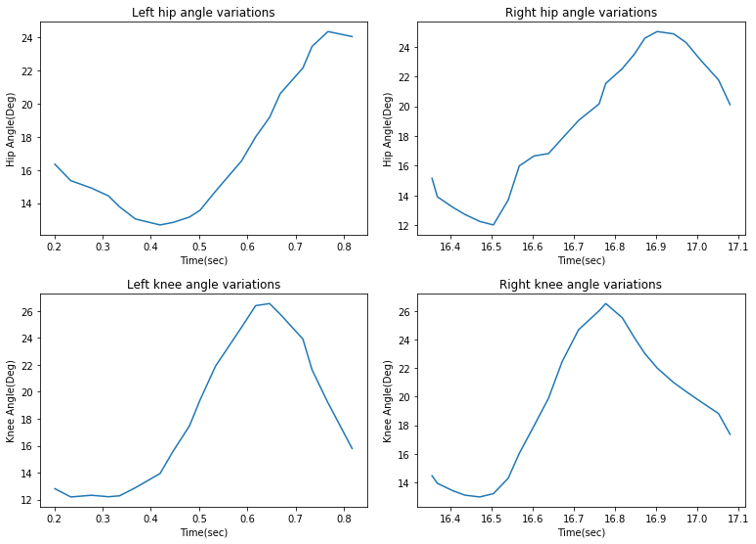
Fig. 5. Range of motion of lower limb, showing the range of motion in the single stride of the left and right hips and left and right knees in the test.
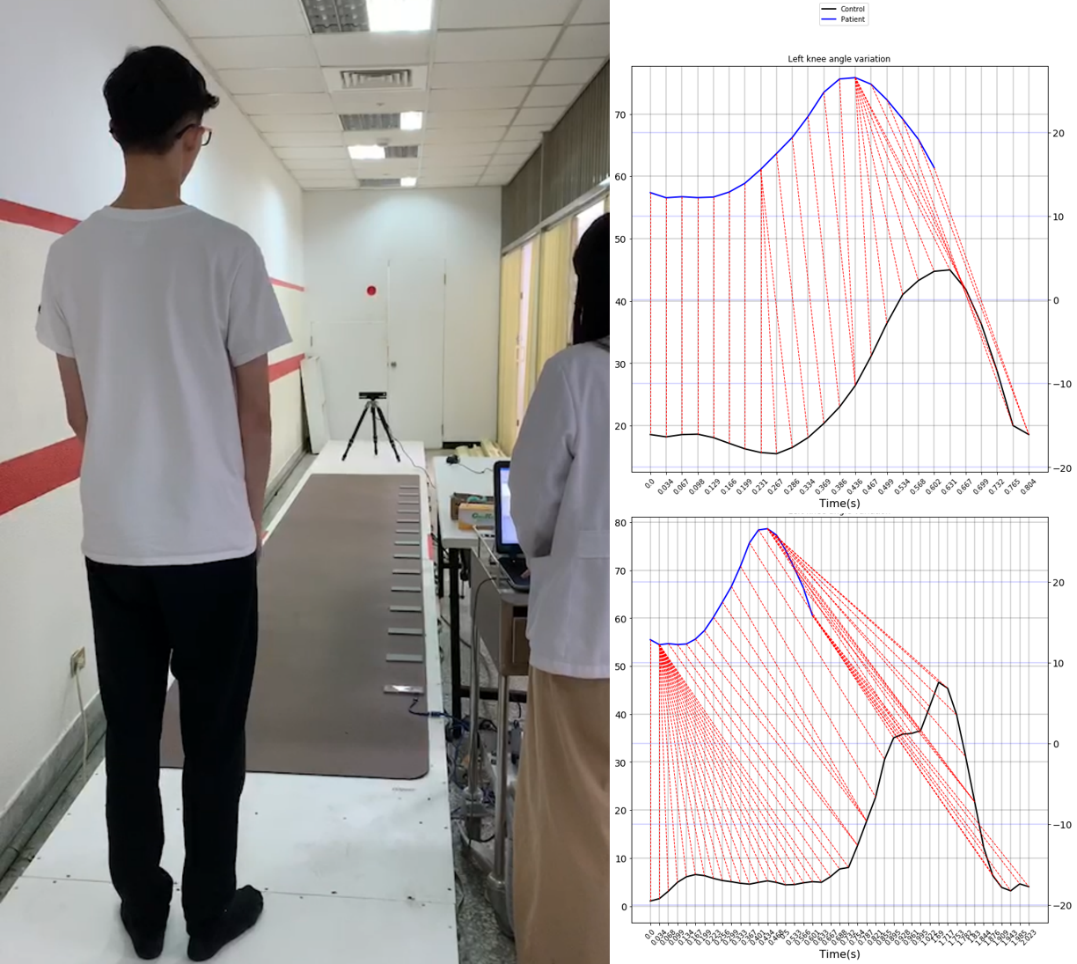
Fig. 6. Dynamic time warping analysis of the knee joint. The left figure shows the subject taking the first test with the medical GaitRite sensor and the Kinect system, and using this result as a baseline for gait detection to achieve rehabilitation results. The blue line curve in the right figure is the result of the first measurement of the subject. In the upper right figure, the subject is compared with the DTW analysis after the first rehabilitation. The DTW distance is 1884.81, the lower right figure compared with the baseline after the second rehabilitation, the DTW distance is 8257.116, which was used to measure the left knee joint movement after the rehabilitation. The rehabilitation quantitative result shows an improvement of 77.17%.
